Cyber Attack
If you are a cybersecurity expert living in today’s shark-infested cyber-world, your mission is to stay ahead of the bad guys and keep your activity safe. This starts by understanding your vulnerabilities, knowing the many ways by which your resistance can be breached, and then putting together in position the protections needed to maintain a secure, tough cybersecurity posture. It’s a big job and is significantly important to the security of your enterprise. Cybercrimes have increased every year as people try to profit from vulnerable business system. Often, attackers are look for liberate 53 percent of cyber-attack resulted in damage. Cyberthreats can also be launched with ulterior motives. Some attackers look to demolish systems and data as a form of “Hacktivism.” Here are three key term that lie at the heart of all enterprise cyber-defenses:
- Attack surface
- Cyber Attack vector
- Security breach
Attack Surface
The sum-total of point on a network where attack can occurs where and not permitted user (the “attacker”) can try to manipulate or take out data using a many of breach methods (the “cyber attack vectors”). If you consider a graph where as the x-axis lists all of the devices and apps on your network (infrastructure, apps, endpoints, IoT, etc.) and the y-axis are the different breach methods such weak and default passwords, reused passwords, phishing, social engineering, unpatched software, mis configurations etc. – the plot is your attack surface
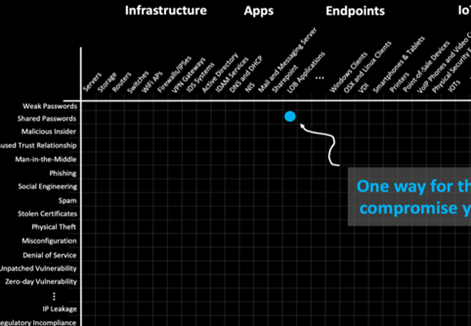
Cyber Attack vector
The method or way by which a challenger can breach or infiltrate an entire system. Attack vectors enable hackers to develop system vulnerabilities, including the human element.

Security breach
Any security incident in which sensitive, protected, or confidential data is accessed or stolen by an unauthorized party, jeopardizing an organization brand, customers, and asset. Incidents such as DDoS, Bitcoin mining etc. are also security breach. Data breaches are the most familiar but not all security incident concern data theft.

Common cyber attack vectors and how to avoid it⌗
Compromised Credentials
The username and password maintain to be the most common type of access credential. Compromised credentials describe a case where user credentials, such as usernames and passwords, are exposed to unauthorized entities. This typically happen when an unsuspecting user fall prey to phishing attempts and type in their login credentials on fake websites.
How to avoid it
Common username and weak password can lead to compromise credentials, so it is to be emphasized that the enterprise has effective password policies that ensure fitting password strength.
Password giving out across services makes all applications that share credential vulnerable as a significance of the breach of one service or application in cohort. Do not reprocess the same password to access multiple apps and systems.
Weak and Stolen Credentials
Weak passwords and password reuse make credential introduction a gateway for initial attackers’ access and propagation. Recent malware attack such as Mirai highlights this threat can not only for manage devices but also IoT connected device.
Apps and protocol sending login credential over the network pose a trivial security threat. An attackers connected to your network can easily locate and utilize these credentials for lateral movement
How to avoid it
Track password hygiene and use across your entire activity to identify high risk user and their device.
Conclusion
So, the goal of an adversary and malicious insider is to access your high value device, apps, and data. Unsecured device and users with access to sensitive app, data, and network will pose a high risk to your enterprise. To stay ahead of the bad guy, you need to start by understand your vulnerabilities, significantly the many ways your defense can be breached, and then putting in place the protection needed to maintain a secure, flexible cybersecurity posture. Keeping the attack surface as small as possible should be considered as a basic security measure and is the key for maintaining a strong attack surface.